Why insurance premiums differ by state

Why insurance premiums differ by state is a complex question influenced by a multitude of factors. Understanding these variations is crucial for consumers seeking the best value and for insurers accurately assessing risk. This exploration delves into the key elements that contribute to this disparity, examining state regulations, risk profiles, economic conditions, market dynamics, and geographical considerations to paint a comprehensive picture of why your premiums might differ based on your location.
From the stringent regulatory environments of some states to the more relaxed approaches of others, the impact on insurance costs is significant. Similarly, factors such as the frequency of claims, the cost of living, and the competitive landscape within a state’s insurance market all play a role in determining premium prices. We will examine real-world examples and data to illustrate how these elements interact and influence the final cost of insurance.
Table of Contents
ToggleState-Specific Regulations and Laws
Insurance premiums vary significantly across states due to differences in regulatory frameworks, mandated coverages, and the level of oversight applied to insurance companies. These variations directly impact the cost consumers pay for insurance.
Impact of State Insurance Regulations on Premium Costs
State insurance regulations establish minimum coverage requirements, dictate how insurers price policies, and influence the overall cost of insurance. More stringent regulations, such as those mandating broader coverage or stricter underwriting guidelines, can lead to higher premiums. Conversely, states with more lenient regulations may have lower premiums but potentially less consumer protection.
Mandated Insurance Coverages and Their Effect on Premiums
The types and extent of mandated insurance coverages vary considerably among states. For example, some states require higher minimum liability limits for auto insurance than others. States with broader mandated coverages, such as those including personal injury protection (PIP) or uninsured/underinsured motorist (UM/UIM) coverage, tend to have higher premiums to account for the increased risk and payout potential.
Regulatory Oversight of Insurance Companies
The degree of regulatory oversight also differs significantly across states. States with robust regulatory agencies and frequent audits may impose stricter compliance requirements on insurers, potentially impacting their operational costs and, consequently, premiums. Conversely, states with less stringent oversight may lead to lower premiums but potentially greater risks for consumers.
Examples of State-Specific Laws Influencing Insurance Pricing
Many state-specific laws directly influence insurance pricing. For example, laws related to tort reform, which limit the amount of damages that can be awarded in lawsuits, can significantly affect auto insurance premiums. Similarly, regulations concerning the use of credit scores in underwriting can also influence premium costs.
Comparison of Key Regulatory Differences Across Five States
| State | Minimum Liability Limits (Auto) | Mandated PIP Coverage | Credit Score Usage in Underwriting |
|---|---|---|---|
| California | $15,000/$30,000 | Optional | Allowed (with restrictions) |
| Texas | $30,000/$60,000 | Optional | Allowed |
| New York | $25,000/$50,000 | Required | Allowed (with restrictions) |
| Florida | $10,000/$20,000 | Required | Allowed |
| Pennsylvania | $15,000/$30,000 | Optional | Allowed (with restrictions) |
Risk Assessment and Claim Frequency
Insurers assess risk at the state level, considering demographic factors and claim frequencies to determine premiums. States with higher claim frequencies, reflecting factors such as weather patterns, crime rates, and driving habits, generally have higher average premiums.
State-Level Demographics and Insurance Risk Assessment
Demographic factors, such as age distribution, population density, and income levels, influence insurance risk assessment. For example, states with a higher proportion of young drivers, who statistically have a higher accident rate, will likely see higher auto insurance premiums.
Correlation Between Claim Frequency and Average Premium
A strong correlation exists between claim frequency in a state and its average insurance premiums. Higher claim frequencies, indicating a greater number of accidents, injuries, or property damage claims, lead to increased payouts for insurers, resulting in higher premiums to offset these costs. This is true across various insurance lines, including auto, home, and health.
Impact of Weather Patterns, Crime Rates, and Driving Habits on Premiums
Several factors contribute to varying claim frequencies across states. States prone to severe weather events, such as hurricanes or tornadoes, experience higher home and auto insurance premiums due to increased damage claims. Similarly, states with high crime rates may have higher home insurance premiums due to increased theft and vandalism claims. States with aggressive driving cultures often have higher auto insurance premiums.
States with High and Low Claim Frequencies
Florida, for example, consistently ranks high in auto insurance premiums due to its high accident rate and frequent severe weather. Conversely, states with lower population densities and more conservative driving cultures may experience lower premiums. Specific data on claim frequencies varies by insurance type and is often proprietary to insurance companies.
Relationship Between Accident Rates and Average Car Insurance Premiums
The following is a textual representation of a chart illustrating the relationship between accident rates and average car insurance premiums across several states. A higher accident rate generally correlates with a higher average premium. Note that other factors beyond accident rates contribute to premium differences.
State | Accident Rate (per 100,000 population) | Average Car Insurance Premium
State A | 500 | $1200
State B | 750 | $1500
State C | 300 | $900
State D | 600 | $1300
State E | 400 | $1000
Cost of Living and Economic Factors
The cost of living, particularly healthcare costs and state taxes, significantly impacts insurance premiums. States with higher costs of living generally have higher insurance premiums, reflecting the increased expense of providing coverage.
Variation in Healthcare Service Costs and Health Insurance Premiums
The cost of healthcare services varies widely across states. States with higher healthcare costs, including higher doctor’s visits, hospital stays, and prescription drug prices, will generally have higher health insurance premiums to cover these increased expenses. This variation is often due to factors like the density of healthcare providers, regulatory environment, and prevalence of chronic diseases.
Impact of State-Specific Taxes on Insurance Company Operational Costs
State-specific taxes, such as premiums taxes and sales taxes, directly affect insurance company operational costs. These taxes are often passed on to consumers in the form of higher premiums. States with higher tax rates generally have higher insurance premiums, all else being equal.
Average Income Levels and Insurance Affordability
Average income levels in different states influence insurance affordability. In states with lower average incomes, insurance may represent a larger portion of household expenses, potentially impacting consumer demand and the ability to pay premiums. This can lead to insurers adjusting pricing strategies or offering more affordable options.
Economic Conditions and Consumer Demand for Insurance
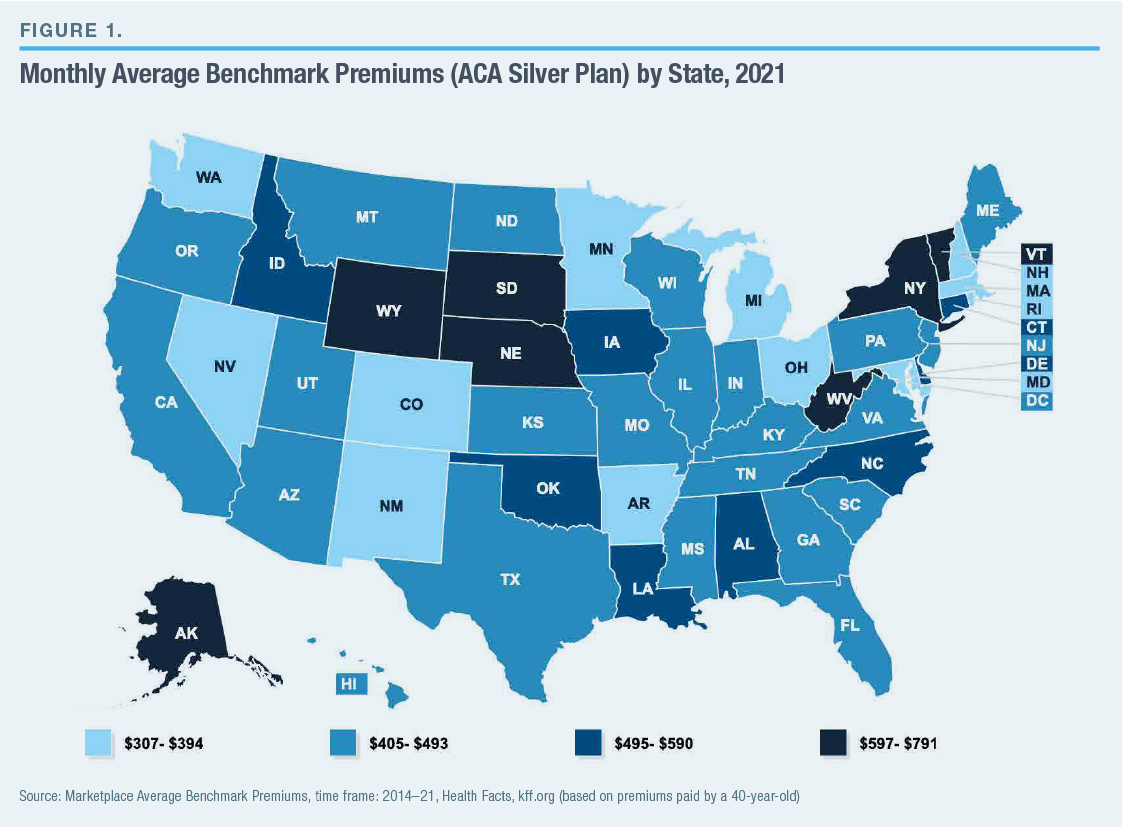
Source: manhattan-institute.org
Economic conditions in a state influence consumer demand for insurance. During economic downturns, consumers may reduce insurance coverage to cut expenses, while during periods of economic growth, demand for insurance may increase.
Economic Factors Influencing Insurance Premiums in High vs. Low Cost-of-Living States, Why insurance premiums differ by state
- High Cost-of-Living States: Higher healthcare costs, higher property values (leading to higher home insurance premiums), higher wages (potentially leading to higher liability insurance premiums), higher taxes.
- Low Cost-of-Living States: Lower healthcare costs, lower property values, lower wages, lower taxes.
Competition and Market Dynamics
The level of competition among insurance providers within a state significantly impacts premium prices. States with a larger number of insurers often experience more competitive pricing, benefiting consumers. Conversely, states with limited competition may have higher premiums due to less price pressure.
Impact of the Number of Insurance Providers on Premium Prices
A higher number of insurance providers typically leads to increased competition, resulting in lower premiums for consumers. This increased competition forces insurers to offer more competitive rates to attract and retain customers.
Market Share of Different Insurance Companies Across Multiple States
The market share of insurance companies varies across states, reflecting the competitive landscape and consumer preferences. Some insurers may dominate certain states while having a smaller presence in others. This market share distribution influences pricing dynamics and consumer choices.
State-Specific Anti-Trust Laws and Regulations
State-specific anti-trust laws and regulations aim to prevent monopolies and promote fair competition in the insurance market. These laws can influence the number of insurers operating in a state and the level of competition, ultimately impacting premium prices. Stricter enforcement of anti-trust laws can foster a more competitive market.
States with High vs. Low Insurance Market Competition
States with highly competitive insurance markets, such as California and Texas, often have lower average premiums than states with less competition. Conversely, states with fewer insurers may have higher premiums due to less price pressure.
Competitive Landscape of the Insurance Market in Three Different States
Let’s consider three states: State A (highly competitive), State B (moderately competitive), and State C (low competition). In State A, multiple large national insurers compete aggressively, leading to lower premiums and diverse product offerings. State B has a mix of national and regional insurers, resulting in moderate competition and average premiums. State C is dominated by one or two major insurers, leading to higher premiums due to limited consumer choice.
Geographic and Environmental Factors: Why Insurance Premiums Differ By State
Geographic location and environmental factors significantly influence insurance risk and premiums. Areas prone to natural disasters, such as hurricanes or earthquakes, typically have higher insurance premiums to reflect the increased risk of property damage and payouts.
Geographic Location and Insurance Risk
Geographic location plays a crucial role in determining insurance risk. Coastal areas prone to hurricanes and flooding will have higher home and auto insurance premiums than inland areas. Similarly, areas situated in earthquake zones will have higher premiums for property insurance. The proximity to wildfire-prone areas also significantly impacts insurance costs.
Impact of Natural Disasters and Climate Change on Insurance Premiums
Natural disasters and climate change significantly impact insurance premiums. The increasing frequency and severity of extreme weather events, such as hurricanes, floods, wildfires, and droughts, lead to higher insurance premiums to offset the increased risk and potential for substantial payouts. Insurers are increasingly incorporating climate change models into their risk assessments.
Geographic Factors Affecting the Cost of Repairing Vehicles or Property

Source: trustedunion.com
Geographic factors also influence the cost of repairing vehicles or property after damage. Areas with limited access to repair services or specialized materials may have higher repair costs, which can indirectly affect insurance premiums. For example, replacing a damaged roof in a remote area may be significantly more expensive than in a densely populated urban center.
Average Cost of Home Insurance in Hurricane-Prone vs. Low-Risk States
States prone to hurricanes, such as Florida and Louisiana, typically have significantly higher average home insurance premiums compared to states with minimal hurricane risk, such as states in the Midwest or Mountain West regions. This difference reflects the increased likelihood of hurricane-related damage and the higher associated costs of repairs and payouts.
Influence of Geographical Factors on Insurance Coverage and Costs
Let’s consider three states: State A (coastal, hurricane-prone), State B (inland, earthquake-prone), and State C (inland, low risk). In State A, flood insurance is often mandatory or highly recommended, significantly increasing premiums. State B may have high earthquake insurance premiums, and specialized coverage may be necessary. State C will have significantly lower premiums across all lines due to the lower risk profile.
The types of coverage offered also vary based on the prevalent risks; for instance, windstorm coverage is crucial in State A, while earthquake coverage is essential in State B.
Final Wrap-Up
In conclusion, the variation in insurance premiums across different states is a multifaceted issue. It’s not simply a matter of one factor but rather a complex interplay of state regulations, risk assessments, economic realities, market competition, and geographical influences. By understanding these contributing factors, consumers can become more informed about their insurance choices and advocate for fairer pricing, while insurers can refine their risk models for greater accuracy and efficiency.
Ultimately, a clearer understanding of this dynamic promotes a more transparent and equitable insurance market for all.
Detailed FAQs
What role does my credit score play in determining my insurance premium?
In many states, credit-based insurance scores are used to assess risk, with higher scores often correlating to lower premiums. This is because individuals with good credit are statistically less likely to file claims.
Can I get a lower premium by bundling my insurance policies?
Yes, many insurers offer discounts for bundling multiple policies, such as auto and home insurance, with the same company. This is a common way to reduce your overall insurance costs.
How often are insurance premiums adjusted?
Premiums are typically adjusted annually, but they can also change more frequently based on factors like driving record changes or claims filed. It is important to review your policy periodically.
What if I move to a different state?
When you move, you’ll need to notify your insurer and they may adjust your premium to reflect the risk profile of your new location. You may also need to switch insurers to find a provider that operates in your new state.